Diatom is an important group of red lineage species in the oceans, which produce around 20% of the primary productivity on the earth. Differing from those in green algae and higher plants, the photosystems of diatoms bind fucoxanthin-chlorophyll a/c binding proteins (FCPs) as peripheral antennas to harvest more blue-green light underwater. FCPs bind unique chlorophyll c, fucoxanthin, diadinoxanthin, diatoxanthin, forming unique pigment networks for energy transfer and photoprotective pathways. Diatoms adapt to light fluctuations rapidly by changing the status of their FCP antennas between efficient light harvesting and super non-photochemical quenching (NPQ).
Scientists from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a structural basis for revealing the energy transfer and dissipation mechanisms and the structural diversity of FCP antennas in the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana.
In this study, the PSII-FCPII-Lhcx6_1 supercomplex was extracted and purified from the thylakoid membranes of the diatom chloroplast. Then its structure was solved by single particle cryo-electron microscopy, which showed that PSII-FCPII-Lhcx6_1 binds monomeric and dimeric FCPII, including a photoprotective family Lhcx6_1.
A photoprotective family protein Lhcx6_1 antenna connects the FCP homodimer to the CP47 side of the PSII core, suggesting that Lhcx6_1 serves as a bridge and transfers the energy from the peripheral FCPII antenna to the core indirectly. Two energy transfer pathways are formed within Lhcx6_1, one transfers the energy through two chlorophyll clusters rapidly to the core, and the other relies on the diadinoxanthin-diatoxanthin cycle to quench excess energy. On the other side of the core, a conserved Lhca2 antenna connects the newly discovered FCP heterodimer to the CP43 side, which is involved in light energy harvesting and transfer.
Compared with previous biochemical and structural analyzes, PsbG was not found in the diatom T. pseudonana, which led to the assembly of different FCP monomer, dimer, or tetramer light-harvesting antennas in the periphery of PSII in different diatom species. The different FCP antennas in different diatoms, combined with different ratios of chlorophyll, fucoxanthin and diatoxanthin, may regulate the light-harvesting, energy transfer and excitation energy quenching in different diatoms, which enabled the diatom PSII-FCPII to better cope with oceanic environments with a changing light environment at a high-frequency .
These results provide a firm structural basis for unraveling the mechanisms of light-energy harvesting, transfer and quenching in the diatom PSII-FCPII, as well as a different structural heterogeneity in the PSII supercomplex.
This study entitled "Structure of a diatom photosystem II supercomplex containing a member of Lhcx family and dimeric FCPII" was published in a paper in Science Advances on October 25th, 2023.
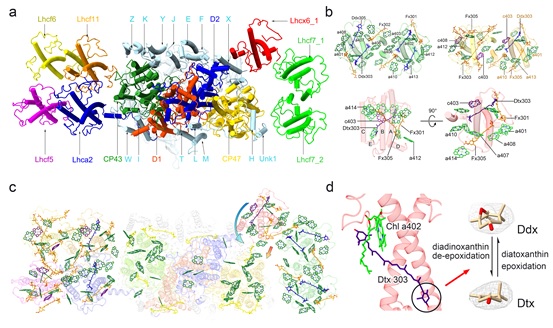
Overall structure and chlorophyll network of the PSII-FCPII-Lhcx6_1 supercomplex. (Image by IBCAS)
Article Link: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adi8446
Contact:
WANG Wenda
Institute of Botany
E-mail: wdwang@ibcas.ac.cn
Diatom is an important group of red lineage species in the oceans, which produce around 20% of the primary productivity on the earth. Differing from those in green algae and higher plants, the photosystems of diatoms bind fucoxanthin-chlorophyll a/c binding proteins (FCPs) as peripheral antennas to harvest more blue-green light underwater. FCPs bind unique chlorophyll c, fucoxanthin, diadinoxanthin, diatoxanthin, forming unique pigment networks for energy transfer and photoprotective pathways. Diatoms adapt to light fluctuations rapidly by changing the status of their FCP antennas between efficient light harvesting and super non-photochemical quenching (NPQ).
Scientists from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a structural basis for revealing the energy transfer and dissipation mechanisms and the structural diversity of FCP antennas in the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana.
In this study, the PSII-FCPII-Lhcx6_1 supercomplex was extracted and purified from the thylakoid membranes of the diatom chloroplast. Then its structure was solved by single particle cryo-electron microscopy, which showed that PSII-FCPII-Lhcx6_1 binds monomeric and dimeric FCPII, including a photoprotective family Lhcx6_1.
A photoprotective family protein Lhcx6_1 antenna connects the FCP homodimer to the CP47 side of the PSII core, suggesting that Lhcx6_1 serves as a bridge and transfers the energy from the peripheral FCPII antenna to the core indirectly. Two energy transfer pathways are formed within Lhcx6_1, one transfers the energy through two chlorophyll clusters rapidly to the core, and the other relies on the diadinoxanthin-diatoxanthin cycle to quench excess energy. On the other side of the core, a conserved Lhca2 antenna connects the newly discovered FCP heterodimer to the CP43 side, which is involved in light energy harvesting and transfer.
Compared with previous biochemical and structural analyzes, PsbG was not found in the diatom T. pseudonana, which led to the assembly of different FCP monomer, dimer, or tetramer light-harvesting antennas in the periphery of PSII in different diatom species. The different FCP antennas in different diatoms, combined with different ratios of chlorophyll, fucoxanthin and diatoxanthin, may regulate the light-harvesting, energy transfer and excitation energy quenching in different diatoms, which enabled the diatom PSII-FCPII to better cope with oceanic environments with a changing light environment at a high-frequency .
These results provide a firm structural basis for unraveling the mechanisms of light-energy harvesting, transfer and quenching in the diatom PSII-FCPII, as well as a different structural heterogeneity in the PSII supercomplex.
This study entitled "Structure of a diatom photosystem II supercomplex containing a member of Lhcx family and dimeric FCPII" was published in a paper in Science Advances on October 25th, 2023.

Overall structure and chlorophyll network of the PSII-FCPII-Lhcx6_1 supercomplex. (Image by IBCAS)
Article Link: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adi8446
Contact:
WANG Wenda
Institute of Botany
E-mail: wdwang@ibcas.ac.cn
